자료구조와 알고리즘이 중요한 이유
재료 - 데이터
도구 - 자료구조
레시피 - 알고리즘
요리 - 소프트웨어
요리사 - 개발자
이 예시 덕분에 각각의 의미와 서로의 관계를 잘 알 수 있었다.
자료구조 + 알고리즘 = 프로그램
자료구조
- 자료구조는 메모리를 효율적으로 사용하여 안정적으로 데이터를 처리하는 것이 궁극적인 목표로 상황에 따라 유용하게 사용될 수 있도록 특정구조를 이루고 있다.
- 즉, 상황에 맞게 자료구조를 선택해야한다. -> but, 메모리를 느리고 불안정하게 처리할 수 있다.
- 리스트, 큐, 스택, 덱, 트리, 그래프 등
알고리즘
- 특정 문제를 효율적이고 빠르게 해결하는 것이 궁극적인 목표로 정해진 일련의 절차나 방법을 공식화한 형태로 표현한 것
- 수학적으로 표현할 수 있다.
- 이진탐색, 최단거리찾기 등
실무에서 중요하게 생각하는 3가지
- 기초 코딩 능력(=문제 해결 능력)
- 자료구조와 알고리즘 공부하기
- 논리적 사고
- 전산화 능력
- 엣지 케이스 탐색(예외 찾는 능력)
- 전문 분야 지식
- 기본 CS 지식
자료구조의 종류
전산화
- 현실에 존재하는 영화 예매를 어떻게 컴퓨터로 옮길 것인가?
- 현실에서 수행되는 프로세스
- 어떤 영화를 볼지 고른다
- 영화를 예매하기 위해 줄을 선다
- 차례가 왔을 때 좌석을 선택한다
- 최종적으로 돈을 지불한다
- 소프트웨어에서 어떻게 처리할 것인가?
- 영화를 검색 -> trie (빠르고 자동완성)
- 고객이 많은 경우 줄을 서야함 -> queue
- 고객은 좌석을 선택할 수 있어야한다 -> hashtable
- 현실에서 수행되는 프로세스
=> 자료구조는 일차원인 컴퓨터 메모리를 현실에 대응되도록 구조를 만든 것
자료구조 종류

- 선형구조 : 한 원소 뒤에 하나의 원소만이 존재하는 형태 → 선형으로 나열 / 배열처럼 앞뒤로 하나밖에 없음
- 비선형구조 : 원소가 다대다 관계를 가지는 구조 → 계층적 구조와 망형 구조를 표현하기에 적합하다 / 컴퓨터폴더구조, 인간관계
시간복잡도
- 프로그램을 성능 측정하는 것은 고려해야할 사항이 많다. (입력 크기, 컴퓨터 성능, 운영체제 성능 등)
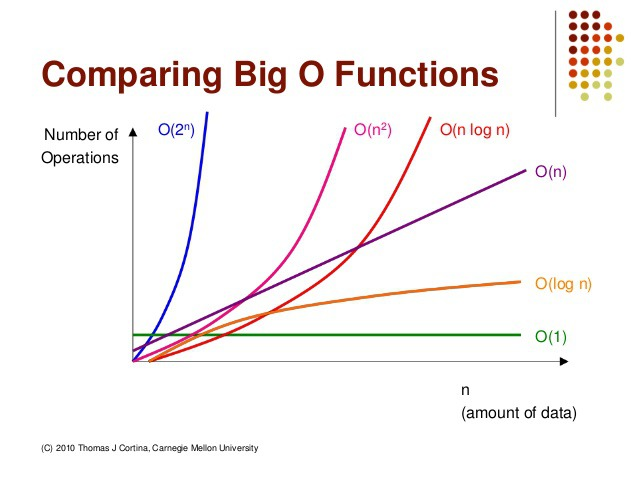
- 이러한 문제를 상대적인 표기법으로 표현한게 big-o 표기법이다.
- big-o 표기법
- 점근적 표기법을 따른다.
- 법칙
- 계수법칙/합의 법칙/곱의 법칙/다항 법칙 → 상수항은 무시하고,가장 큰항을 제외하고 무시
- 순서 : O(1) < O(logn) < O(n) < O(nlogn) < O(n^2) < O(2^n) <O(n!)
- O(f(n))에서 f(n)이 1에 가까울 수록 성능이 좋다고 판단한다.
- f(n)은 로직이 반복되는 횟수라고 이해할 수 있는데, 예를 들어 반복문을 n번돌리는 로직이다 라고한다면 O(n)이라고 쓸 수 있는 것이다.
- 일반적으로 가능하다면 O(nlogn)까지 시간 복잡도를 줄이는 방향으로 코드를 짜는 것이 바람직 하다고 한다.
- 그리고 f(n)은 최고차항만 계수를 때고 고려를 하는데, 예를 들어 f(n) = 3n^3 + 6n^2 + 2n 이라고 할 때, f(n)을 O(n^3)이라고 취급할 수 있다는 뜻이다. 그 이유는 n이 굉장히 큰 수라고 할 경우 사실 f(n)에 영향을 가장 크게 끼치는 부분이 n^3 이기 때문이다.
성능 측정 방법
- js의 Date 객체 이용 : 시작시간을 구하고 로직을 돌려 끝시간에서 시작시간을 빼주면 로직이 작동한 시간을 알 수 있다.
배열
- 연관된 데이터를 연속적인 형태로 구성된 구조
- 특징
- 고정된 크기를 가지며 일반적으론 동적으로 크기를 늘릴 수 없다.
→ 자바스크립트처럼 대부분의 스크립트 언어는 동적으로 크기가 증감되도록 만들어져 있다. - 탐색 : 원하는 원소의 index를 알고 있다면 O(1)로 원소를 찾을 수 있다.
- 삭제,추가(중간에) : O(n) → 데이터를 추가하고 하나씩 옮겨야해서 선형시간이 나온다.
- 원소를 삭제하면 해당 index에 빈자리가 생긴다.
- 고정된 크기를 가지며 일반적으론 동적으로 크기를 늘릴 수 없다.
연결 리스트

- 연결 리스트는 각 요소를 포인터로 연결하여 관리하는 선형 자료구조를 의미한다.
- 각 요소는 노드라고 부르며 데이터 영역과 포인터 영역으로 구성된다.
- 특징
- 메모리가 허용되는 한 제한없이 추가가 가능하다.
- 탐색 : O(n) → 하나씩 탐색
- 추가,삭제 : O(1) → 추가/삭제를 위한 탐색을 하지 않도록 코드 작성시
- 추가 / 삭제 시 자주 일어날시 사용되는 자료구조
- 배열과 연결 리스트의 메모리 차이
- 배열은 메모리에 순차적으로 들어가지만 연결 리스트는 순차적이지 않고 각 데이터가 퍼져 있다.
- 포인터를 사용하여 각 영역을 참조하게 된다.
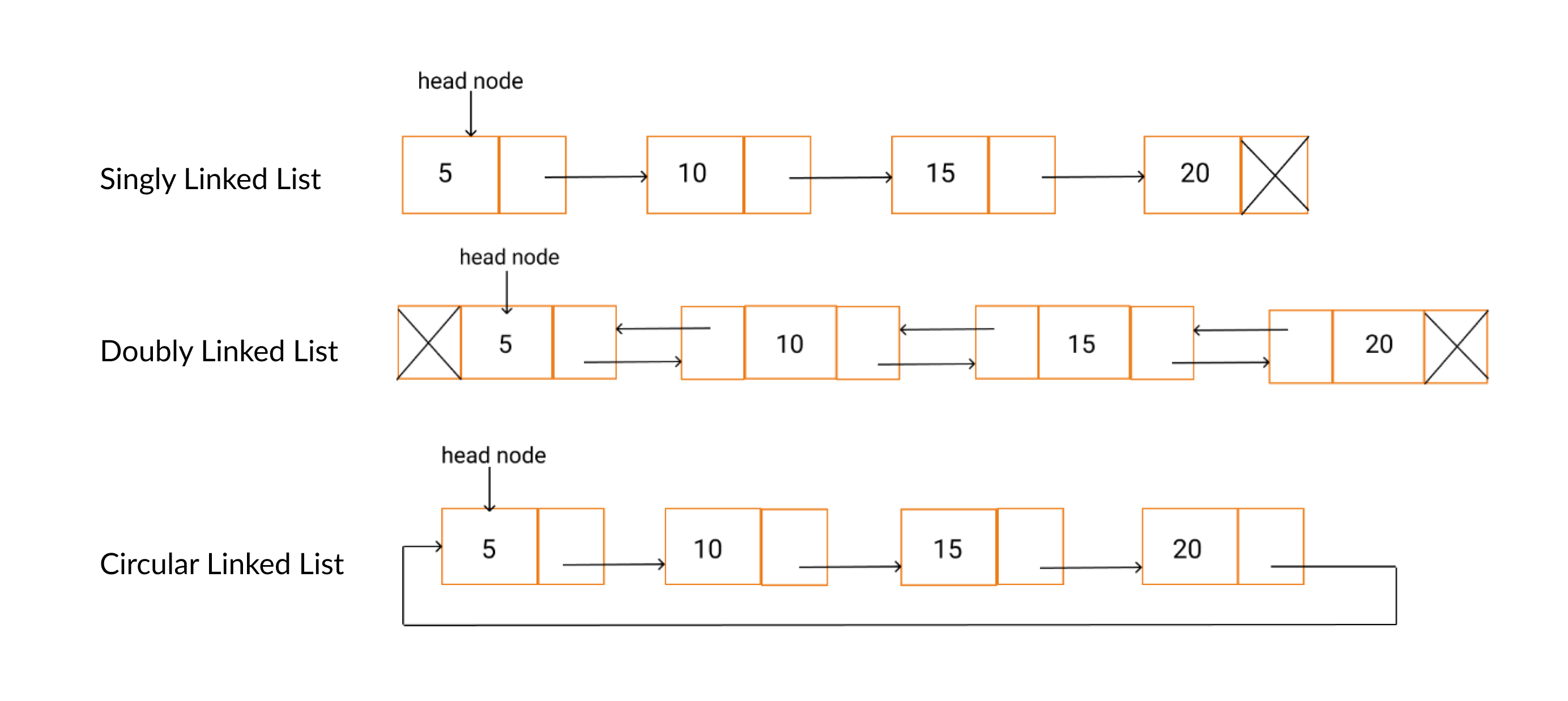
단일 연결 리스트 Singly Linked List
- HEAD → Tail까지 단방향으로 이루어지는 자료구조
- remove시 자동으로 가비지컬렉터에 의해서 사라진다.
- 요소 찾기
- 헤드부터 포인터를 따라가며 하나씩 찾아보는 수밖에 없다.
- O(n) 선형 시간이 소요된다.
- 요소 추가
- O(1) 상수 시간만 소요된다.
- 추가를 위한 탐색을 하지 않도록 코드를 주의해서 작성해야 한다!!!
- 요소 삭제
- O(1) 상수 시간만 소요 된다.
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
class SingleLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
find(data) {
let curNode = this.head;
while (curNode.data !== data) {
// 없을시 예외처리
if (curNode === this.tail) return null;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return curNode;
}
append(data) {
const newNode = new Node(data);
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
}
add(node, data) {
// 찾는 노드가 없을시 예외처리
if (node !== null) {
const newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = node.next;
node.next = newNode;
}
}
remove(data) {
let preNode = this.head;
// 데이터가 젤 처음에 등장했을때 예외처리
if (preNode.data === data) {
this.head = preNode.next;
return;
}
while (preNode.next.data !== data) {
preNode = preNode.next;
// 다음이 없을때 예외처리
if (preNode.next === null) return null;
}
if (preNode.data !== null) {
preNode.next = preNode.next.next;
}
}
size() {
let cnt = 0;
let curNode = this.head;
while (curNode !== null) {
curNode = curNode.next;
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
display() {
let ret = "[";
let curNode = this.head;
while (curNode !== null) {
ret += `${curNode.data},`;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
ret = ret.substring(0, ret.length - 1);
ret += "]";
return ret;
}
}
const singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList();
singleLinkedList.append(1);
singleLinkedList.append(2);
singleLinkedList.append(3);
singleLinkedList.remove(1);
singleLinkedList.remove(2);
console.log(singleLinkedList.display());
singleLinkedList.add(singleLinkedList.find(1), 2);
console.log(singleLinkedList.display());
console.log(singleLinkedList.size());
이중 연결 리스트 Doubly Linked List
- 양방향으로 이어지는 연결리스트
- 단일 연결 리스트와 다르게 각 노드에 포인터가 2개 존재한다.
- 자료구조가 단일 연결 리스트 보다 좀 더 크다.
- 요소 추가와 삭제
- O(1) 상수 시간만 소요된다.
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.pre = null;
this.next = null;
}
}
class DoubleLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
find(data) {
let curNode = this.head;
while (curNode.data !== data) {
if (curNode === this.tail) return null;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return curNode;
}
append(data) {
const newNode = new Node(data);
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.pre = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
}
}
add(node, data) {
if (node !== undefined) {
const newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.pre = node;
newNode.next = node.next;
node.next = newNode;
if (newNode.next !== null) {
newNode.next.pre = newNode;
}
// node.next.pre = newNode;
} else {
return null;
}
}
remove(data) {
let preNode = this.head;
if (preNode.data === data) {
this.head = preNode.next;
if (preNode.next !== null) {
preNode.next.pre = null;
}
return;
}
while (preNode.next.data !== data) {
preNode = preNode.next;
if (preNode.next === null) return null;
}
if (preNode.data !== null) {
preNode.next = preNode.next.next;
if (preNode.next !== null) {
preNode.next.pre = preNode;
}
}
}
size() {
let cnt = 0;
let curNode = this.head;
while (curNode !== null) {
curNode = curNode.next;
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
display() {
let ret = "[";
let curNode = this.head;
while (curNode !== null) {
ret += `${curNode.data},`;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
ret = ret.substring(0, ret.length - 1);
ret += "]";
return ret;
}
}
const doubleLinkedList = new DoubleLinkedList();
doubleLinkedList.append(1);
doubleLinkedList.append(2);
doubleLinkedList.append(3);
doubleLinkedList.remove(1);
// console.log(doubleLinkedList.)
console.log(doubleLinkedList.display());
환형 연결 리스트 circular Linked List
- 단일 혹은 이중 연결 리스트에서 Tail이 Head로 연결되는 연결 리스트이다.
- 중간에서 탐색을 시작하더라도 한 바퀴를 전부 탐색할 수 있다.
- 메모리를 아껴 쓸 수 있다는 장점이 있다.
- 원형 큐 등을 만들 때도 사용한다.
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
class CircularLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
find(data) {
let curNode = this.head;
while (curNode.data !== data) {
if (curNode.next === this.head) return null;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return curNode;
}
append(data) {
const newNode = new Node(data);
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
newNode.next = this.head;
}
}
add(node, data) {
if (node !== null) {
const newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = node.next;
node.next = newNode;
return;
}
}
remove(data) {
let preNode = this.head;
if (preNode.data === data) {
this.head = preNode.next;
return;
}
while (preNode.next.data !== data) {
preNode = preNode.next;
if (preNode.next === this.head) return null;
}
if (preNode.data !== null) {
if (preNode.next === this.tail) {
this.tail = preNode;
preNode.next = this.head;
}
else
preNode.next = preNode.next.next;
}
}
size() {
let cnt = 0;
let curNode = this.head;
while (curNode !== null) {
cnt++;
if (curNode === this.tail) break;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return cnt;
}
display() {
let ret = "[";
let curNode = this.head;
while (curNode !== null) {
ret += `${curNode.data},`;
if (curNode === this.tail) break;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
ret = ret.substring(0, ret.length - 1);
ret += "]";
return ret;
}
}
const circularLinkedList = new CircularLinkedList();
circularLinkedList.append(1);
circularLinkedList.append(2);
circularLinkedList.append(3);
circularLinkedList.add(circularLinkedList.find(1), 5);
circularLinkedList.remove(1);
console.log(circularLinkedList.size());
스택
- 스택은 LIFO구조이다. LIFO 구조란 Last In First Out의 약자로, 맨 나중에 들어간 자료부터 순서대로 꺼낸다는 뜻
- 우리가 상자에 물건을 넣으면 꺼낼때는 맨 위의 물건 부터 꺼내는 것과 같이, 맨 나중에 들어간 데이터부터 꺼내는 자료구조이다.
- 프링글스
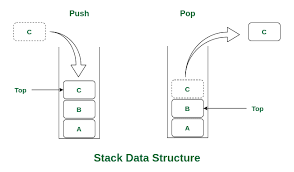
Stack을 Array로 표현하기
const stack = []
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
console.log(stack); // [1, 2, 3]
stack.pop();
console.log(stack); // [1, 2]
console.log(stack[stack.length - 1]); //2Stack을 Linked List로 구현
- 연결리스트의 head가 스택의 top이 된다.
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.top = null;
this.size = 0;
}
push(value) {
const node = new Node(value);
node.next = this.top;
this.top = node;
this.size += 1;
}
pop() {
const value = this.top.value;
this.top = this.top.next;
this.size -= 1;
return value;
}
size() {
return this.size;
}
}
const stack = new Stack();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
console.log(stack.pop()); //3
stack.push(4);
console.log(stack.pop()); //4
console.log(stack.pop()); //2'데브코스 프론트엔드 5기 > JavaScript 주요 문법' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 230927 [Day7] JavaScript 주요 문법 (6) (0) | 2023.09.27 |
|---|---|
| 230926 [Day6] JavaScript 주요 문법 (5) (0) | 2023.09.26 |
| 230925 [Day5] JavaScript 주요 문법 (4) (0) | 2023.09.25 |
| 230921 [Day3] JavaScript 주요 문법 (2) (0) | 2023.09.22 |
| 230920 [Day2] JavaScript 주요 문법 (1) (0) | 2023.09.20 |